Product Search
Silicones for Coatings
4 usages of silicones for coating agents
Use 1 Silicone based ResinsUsed as the resin itself
Silicone Resins
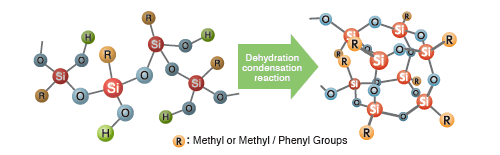
- Structure:
- Resin having a high molecular weight and three-dimensional siloxane network structure.
- Features:
- With excellent film-forming abilities, coatings can range from very hard to flexible.
Silicone Oligomers (Type A)
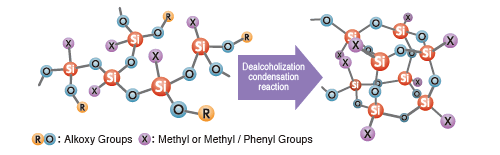
- Structure:
- Resin having a relatively low molecular weight and three-dimensional siloxane network structure. Molecules contain alkoxy groups and non-reactive functional groups.
- Features:
- Can be used on their own, or to modify organic resins. Can also be used as reactive diluents.
Features
Catalog
Use 2 Resin Hybridization AgentsUsed to improve other resins and impart them with the properties of silicones
Silane Coupling Agents
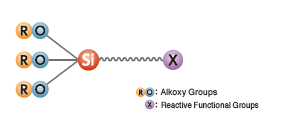
- Structure:
- Monomer whose molecules contain alkoxy groups and reactive functional groups.
- Features:
- While alkoxy groups improve adhesion to inorganic materials, reactive functional groups improve adhesion to organic materials.
Silicone Oligomers
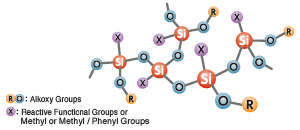
- Structure:
- Oligomer having three-dimensional siloxane network structure. Molecules contain alkoxy groups and reactive functional groups.
- Features:
- Can also be used for modification of organic resins, or even as a reactive diluent.
Silicone Resins
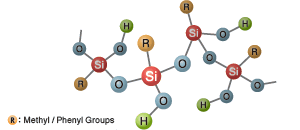
- Structure:
- Resin having a high molecular weight and three-dimensional siloxane network structure.
- Features:
- With excellent film-forming abilities, coatings can range from very hard to flexible.
Modified Silicone Fluids
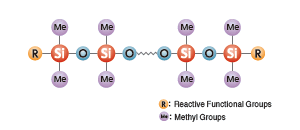
- Structure:
- Two-dimensional siloxane main chain with reactive or non-reactive functional groups in the side chains and ends.
- Features:
- Silicone fluids having reactive functional groups can be used for modification of organic resins.
Resulting Properties
Acrylic Resins
Epoxy Resins
Polyester & Alkyd Resins
Urethane Resins
Catalog
Use 3 Surface Modifiers for Coatings Used as additives to improve the surface conditions of coatings
Silicone Powders
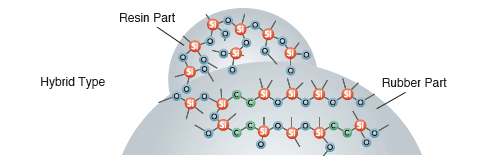
- Structure (3 types):
- Resin, rubber & resin coated rubber
- Features:
- Available in a variety of particle sizes and shapes, to meet a range of requirements.
Resulting Properties
KP Series
- Features:
- Coating Surface Modifiers designed for use as leveling agents, defoamers, slicking agents, and in coatings.
Resulting Properties
Catalog
Use 4 Surface Modifiers for Pigments & Fillers Used to modify the surface of fillers to improve coating performance
Alkoxy Silanes
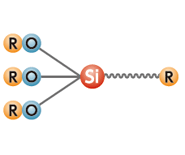
- Structure:
- Monomer whose molecules contain alkoxy groups.
- Features:
- Alkoxy groups act to improve adhesion to inorganic materials.
Resulting Properties
Silane Coupling Agents
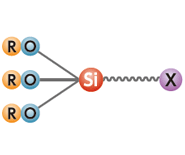
- Structure:
- Monomer whose molecules contain alkoxy groups and reactive functional groups.
- Features:
- While alkoxy groups improve adhesion to inorganic materials, reactive functional groups improve adhesion to organic materials.
Resulting Properties
Spherical Silica Fine Particles
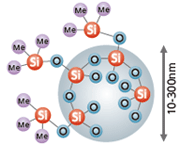
- Structure:
- Very small particle size with narrow particle size distribution. Particle surfaces treated to give them extra water repellency.
- Features:
- Monodisperse, less aggregation. Fine adhesion to various powders, and improves flowability.

